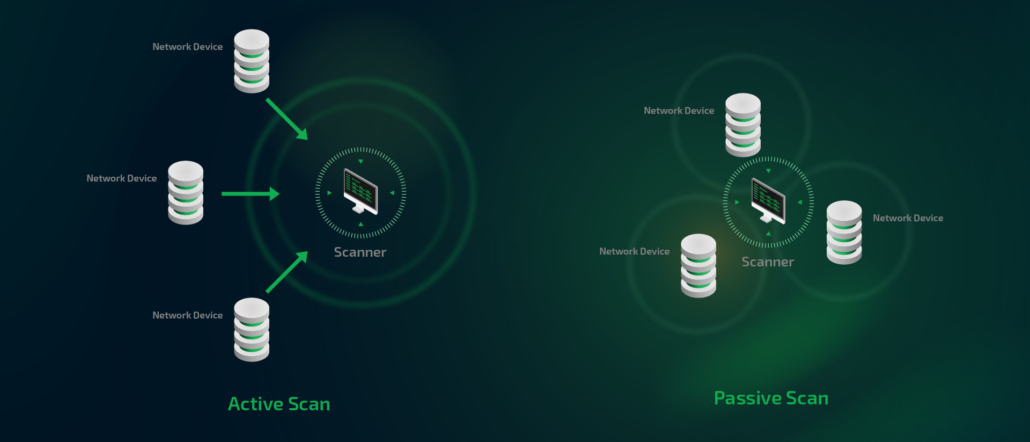
Greenbone, the global leader in open source vulnerability management solutions, has launched a community portal for its user and developer community, making the extensive information available for community editions clearer and easier to access.
Who is the portal for?
At community.greenbone.net, vulnerability management experts invite users, developers and all IT professionals who are professionally involved in security and protection against hackers to browse forums, blogs, news and documentation and help shape the pages.
Central point of contact
“Our new Community Portal is the central place where users, experts, Greenbone employees and anyone else interested can meet and get up-to-the-minute information about the products, the company or new features,” explains Greenbone’s Community Manager DeeAnn Little: “We want the portal to be a home for the large, worldwide Greenbone community, with all the links and information anyone who works with our vulnerability management tools needs.”
What the new portal offers
For both Greenbone OpenVAS and the Greenbone Community Edition, you can find (under “Getting started“) numerous instructions on how to install and configure the community versions. In addition, there are news and updates, for example about the recently released Docker container releases of the Community Edition but also current figures about Greenbone installations on a world map and a completely revised forum with new categories and Blog.
For the community, with the community
“All this would not be possible without the numerous contributions from the Greenbone community, but at the same time this is only the first step,” explains Little: “In the future, we will also have our experts explain technical details and present new features here.
Greenbone invites the large community to give input and suggestions which topics are of relevance and interest for them Little explains:
“We welcome all input and all suggestions, ideas and ideas for improvement, which is exactly what the portal is here for. Send us your questions, any questions! What have we missed? What would you like to see? How can we make the portal, the forum and the new pages even better? What topics would you like to see – what should we report on?” You can leave your statement here, we will be glad to reveive it.
Greenbone Community Forum in a new look
Greenbone has also integrated the popular User Forum into the Community Portal. With the new look, it will continue to provide users of Greenbone’s software – regardless of their technical background – with a platform for ideas, mutual help, but also feedback.
“The forum is a place where users can meet and help each other as equals – it’s a place of exchange where we can always learn, too,” Little explains. “Whether it’s a beginner’s question, more in-depth howtos, or getting started guides, many a user will find help from experienced users in the forum, even in exotic setups.”